Electrodessication is often used for the treatment of common skin conditions such as Seborrheic Keratoses (SK), Dermatosis Papulosa Nigricans (DPN) and Sebaceous Hyperplasia (SH). Electrodessication is a medical procedure that employs electrical currents to remove or treat various skin lesions, offering a safe and effective solution for these benign growths.
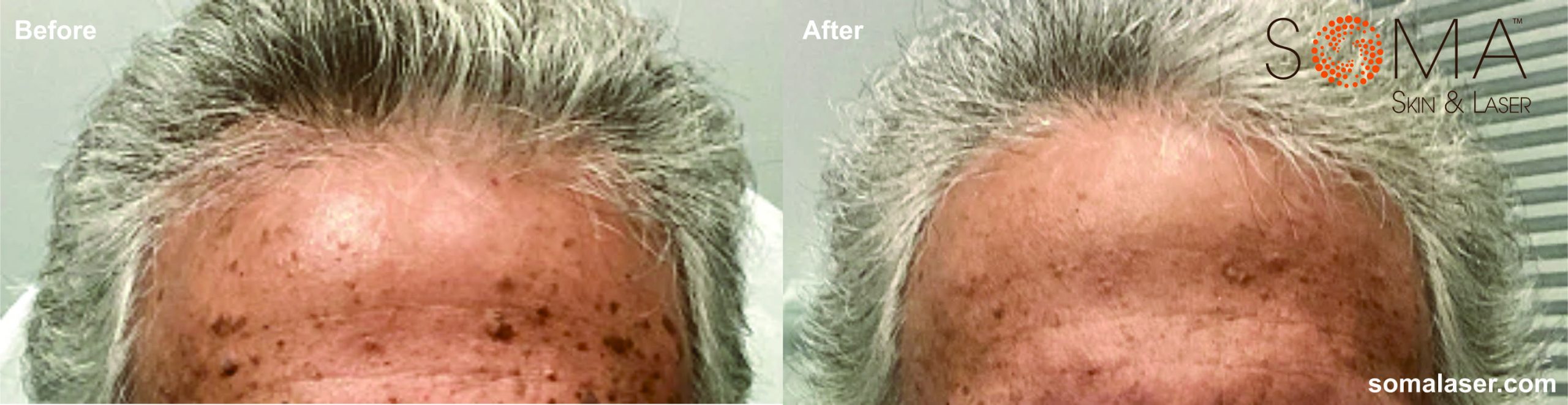
Disclaimer: Results may vary patient to patient. There is no guarantee that any specific result can be achieved. Results may not be permanent.
Understanding Seborrheic Keratoses and Dermatosis Papulosa Nigricans
- Seborrheic Keratoses (SK): These are non-cancerous, wart-like skin growths that can appear in various colors, usually on the face, chest, shoulders, or back. SKs are common with age and are typically harmless but can be aesthetically bothersome.
- Dermatosis Papulosa Nigricans (DPN): DPN is characterized by small, brown to black raised lesions that often occur on the neck, armpits, and other body areas. Like SKs, DPN is benign but can be a cosmetic concern.
- Sebaceous Hyperplasia (SH): Sebaceous hyperplasia involves enlarged sebaceous (oil) glands, typically appearing as small, yellowish bumps on the face. While benign, these bumps can be a cosmetic concern, particularly as they become more prominent with age.
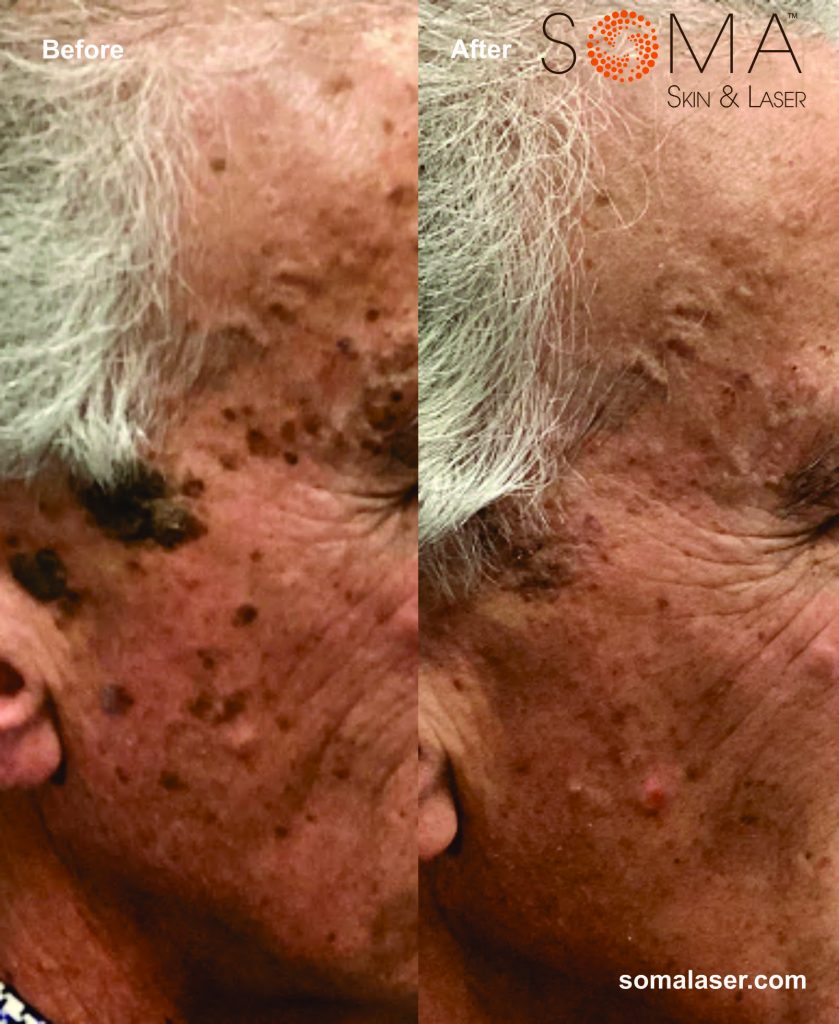
Disclaimer: Results may vary patient to patient. There is no guarantee that any specific result can be achieved. Results may not be permanent.
The Role of Electrodessication
Electrodessication involves using a high-frequency electrical current to dehydrate and destroy targeted tissue. This technique is particularly effective for the removal of benign skin lesions, offering precision and minimal scarring. It is one option for treating benign skin lesions. Sometimes laser treatment with the GentleLase, Revlite, or DEKA SmartXide DOT may be used as well.
Advantages of Electrodessication
Precision: Electrodessication allows for precise targeting of lesions, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Quick Procedure: The procedure is generally quick, often performed in an outpatient setting, with minimal downtime for patients.
Low Risk of Scarring: Compared to other surgical methods, electrodessication tends to result in minimal scarring, promoting better cosmetic outcomes.
The Electrodessication Procedure
Consultation: A dermatologist will assess the lesions to determine their nature and whether electrodessication is a suitable treatment.
Preparation: The skin is typically cleaned, and a local anesthetic may be applied to ensure patient comfort during the procedure.
Electrodessication: The dermatologist uses a specialized device to deliver electrical currents to the targeted lesions, effectively removing or treating them.
Post-Procedure Care: Following the procedure, patients may experience some redness or scabbing, but these side effects are temporary. Dermatologists provide guidelines for proper aftercare to promote optimal healing.
Post-Treatment Expectations
Temporary Redness: Mild redness is common and usually subsides within a few days.
Scabbing: The treated areas may form scabs, which should be allowed to heal naturally.
Follow-up Appointments: Patients may be scheduled for follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress and address any concerns.
Conclusion
Electrodessication is a reliable and efficient option for treating Seborrheic Keratoses, Dermatosis Papulosa Nigricans and Sebaceous Hyperplasia. If you are considering this procedure, consult with a qualified dermatologist to discuss your specific case and determine the most appropriate course of action for achieving clear and healthy skin.
